Una rappresentazione parametrica omogenea della retta
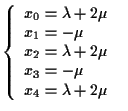 con
con
Un'equazione cartesiana per
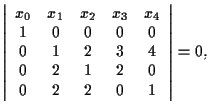 cioè
cioè
 ovvero
ovvero
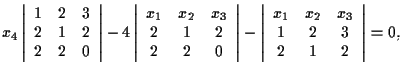 cioè
cioè
Quindi
Il punto di intersezione della retta e dell'iperpiano ha pertanto coordinate proiettive omogenee
Soluzione
Una rappresentazione parametrica omogenea della retta ![]() è
è
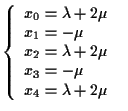 con
con
![]()
Un'equazione cartesiana per ![]() è data (vedi esempio 14) da
è data (vedi esempio 14) da
 cioè
cioè
 ovvero
ovvero
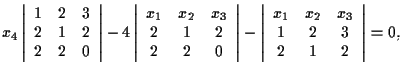 cioè
cioè
![]() ossia
ossia
![]() cioè
cioè
![]()
![]() equazione cartesiana di
equazione cartesiana di ![]()
Quindi
![]() cioè
cioè
![]()
Il punto di intersezione della retta e dell'iperpiano ha pertanto coordinate
proiettive omogenee
![]() con
con
![]() è cioè il punto
è cioè il punto
![]()